
When Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web, he envisioned a single software package that allowed everyone to create and read pages across the internet. Much has happened in the intervening years, but this idea is starting to come back.
Many of the web's founders now realize that they didn't sign up for a web dominated by a few giant corporations relying on collecting massive amounts of data on its users to sell to advertisers.
The Beaker Browser project is creating a decentralized peer-to-peer web browser that, if successful, could return the web to its users. Let's explore how this is done!
Beaker Browser serves as a bridge to a possible future for the web—and the internet. You can use Beaker today to surf the web like any other Chromium-based browser. More important, you also can use Beaker to create and support a new, decentralized, server-less internet.
Beaker Browser uses a peer-to-peer network protocol called Dat to create a decentralized web platform. Websites spread from people seeding them, BitTorrent-style. When following news and discussions about the decentralized web, you'll often hear about blockchain as an underlying basis. The Beaker team thinks that blockchain negotiations and "proof of work" requirements unnecessarily slow down the web. It's better to build "communities of trust" among peers than to try to eliminate trust altogether.
Centralized servers, internet service providers and web hosting firms restrict the options for users to collaborate with one another to build a better world. Comcast, AT&T and cable companies seek to end the principle of net neutrality to narrow the content choices users have always made on their own. At the same time, Facebook, Amazon, Google and other giant content corporations seek to keep us locked inside their respective walled gardens, persuading us that they have all the content we'll ever need. There's no need to visit the open internet. Both sides of this corporate clash do this to maximize profits for themselves.
Users deserve better, and Linux users want all the choices.
The Dat Project describes itself as "Modeled after the best parts of Git, BitTorrent, and the internet, the Dat protocol is a peer-to-peer protocol for syncing files and data across distributed networks."
Dat began as a file-sharing protocol, designed to allow users to store and share encrypted files without using centralized services like Dropbox. With the Dat Desktop app, you can make any folder on your system use the Dat protocol. Every file in that folder is encrypted with a private key. Dat also allows for storing version information for each file shared on the network.
The easy way to install v0.8 of Beaker is to head to https://beakerbrowser.com/download and pick up the AppImage. You can get browsers for Mac and Windows here as well. To stay on the bleeding edge, grab and compile the latest source from GitHub: https://github.com/beakerbrowser/beaker.
Note: Beaker is a 64-bit application. If you run a 32-bit Linux, you're out of luck for the moment.
If you haven't used AppImage to install software yet, you may find this process smile-inducing. Just make the image file executable. You then can run it from the shell or GUI file manager. Beaker will ask to integrate with your existing desktop environment, adding itself to your app launcher for easy access.
Beaker is based on Chromium, so the user interface should be reasonably familiar. The default start page (beaker://start/) has a search dialog and a set of default Pinned Bookmarks. Following these links will give you a pretty good introduction to the Beaker project and the peer-to-peer web. Note that right-clicking on any element on a page offers an Inspect Element option to open Developer Tools. Now you're ready to browse.
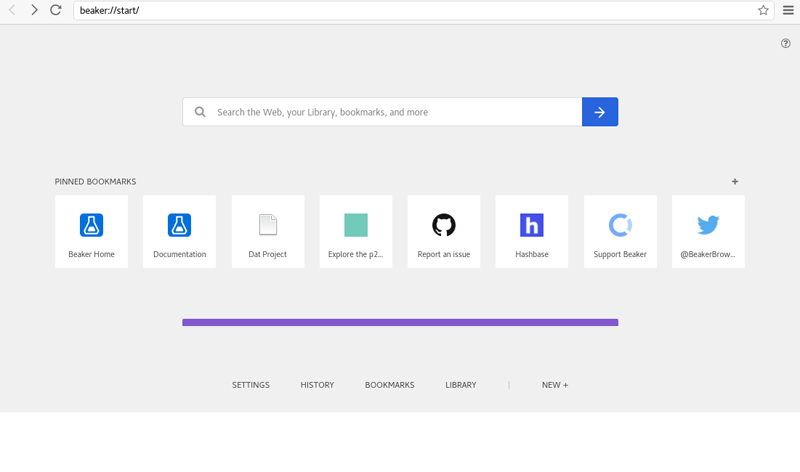
Figure 1. Learn more about Beaker and the peer-to-peer web on the default Beaker://start page.
Note: the screenshots in this article were taken from Beaker on openSUSE Leap 15.
Entering any standard web address in Beaker will display exactly as it would in another browser, so that's not especially interesting. Where you begin to see the bridge to the future is when you look at a Dat-based page.
Start out by visiting the HTTPS-based Take a Tour intro page. On the right side of the address bar, you'll see that this page has a P2P version available. Click that button to see the Dat version of the page. The page display should be identical to the HTTPS site. The differences are subtle. The lock icon on the HTTPS site is replaced by a Share icon; click the icon for a pointer to the Beaker wiki on GitHub for more information. Because this page supports both Dat and HTTP, you'll see the inverse Go to HTTP/S version button too.
A peer-to-peer network like BitTorrent and Dat depends on individuals sharing files with each other. You don't need a server to contain all the content, just some folks willing to help out. On the right end of Beaker's address bar, you'll see another share icon, with the number of peer sites that currently are sharing this site with you. Click that icon, and you can join the peer-to-peer network, also called a swarm. By default, you're sharing the page only while you're visiting. The box tells you the size of the page. You can select a longer period of time to seed the page with the slider: a day, week, month or forever.
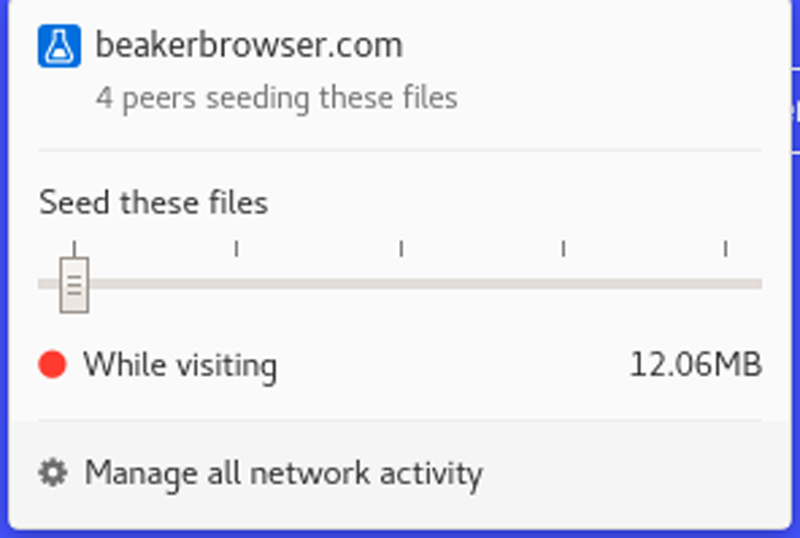
Figure 2. Keep this site online when you seed it on your computer.
When you seed a site, Beaker stores a read-only copy of the page in your /home directory (in openSUSE, it's inside .config/Beaker Browser). Seeded sites also go into Beaker's Library, along with the sites you make. You then can search your Library for relevant content.
Click the three vertical dots menu next to the shares site count to access a ton of details about the site. Choose the View Source option.
The first thing you're likely to notice is the Dat link for the page in the address bar. This is a 64-character public key identifier that never changes. The link encrypts every file being transferred, controls access to the archived files and includes version history. Whoever created the Dat link created (and stores) the private key for that link/content. This makes a Dat link more secure than even an IP address transported via HTTPS. Side benefit: you don't need to persuade system administrators to enable a new IP protocol to identify computers on a network. We have seen how the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has gone to date.
The Files tab connects with everything connected to the page content. Click Seed to spread the site to other places. Click Make an Editable Copy to download a copy of the site (or portions of it) to edit.
Click the Network tab to identify who else is seeding the site. You can use this page to see what IP addresses are sharing, and use the Swarm Debugger to see if those sharing sites are credible and trustworthy.
Click the About tab to get a description of the site and a downloadable copy of the Favicon sitting in the corner of the browser.
When Tim Berners-Lee invented the web, his browser also could write and edit pages. Beaker's founder, Paul Frazee, originally wanted his browser to work the same way. He quickly realized that most web developers today have their own favorite editor. Beaker still provides an editor, but you also can import web files from any editor to create a website.
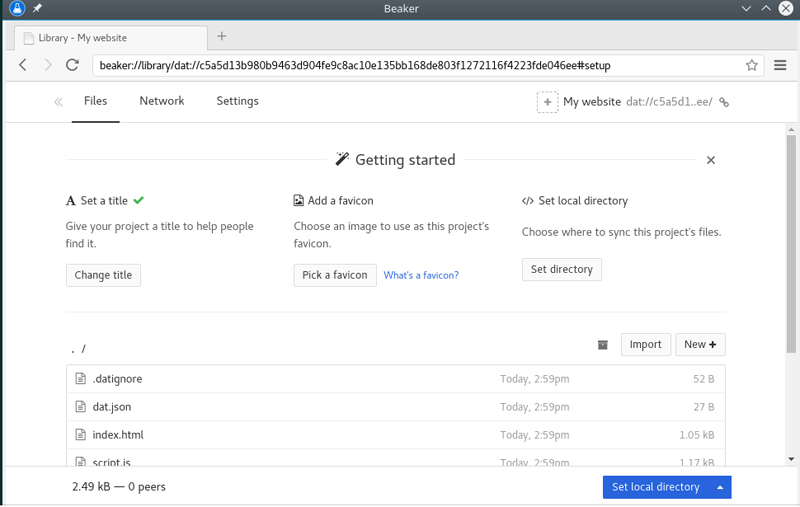
Figure 3. Create and edit peer-to-peer websites. You can share files too!
To create a Dat-based website in Beaker:
These files remain on your system only until you are ready to share the site with the world (or some subset of it). You can continue writing and editing files in the project folder as long as you choose. Change the project title and Favicon on the Settings page.
Now you've made your website, and you want to make sure everyone sees it. And by "everyone", I mean "people who can't see Dat links". The problem is that if you enter dat://beakerbrowser.com into Firefox, the browser may deliver a Google search page. Among the results is https://beakerbrowser.com, and you start wondering how that got there. If you already have Beaker installed, Firefox will suggest opening Dat links with Beaker.
Beaker supports the /.well-known web convention, and you can set this up to create an HTTPS version of your site. An easy way to do this is to copy some already shared files from beakerbrowser.com. Here's how:
Beaker developer Tara Vancil describes what's going on underneath like this:
Beaker piggybacks off of DNS authentication in combination with the /.well-known convention to enable dat:// shortnames. When you visit dat://taravancil.com in Beaker, it sends a request to https://taravancil.com/.well-known/dat and expects to find a file that looks like this: dat://6dff5cff6d3fba2bbf08b2b50a9c49e95206cf0e34b1a48619a0b9531d8eb256/TTL=3600
Because Beaker can trust the DNS resolution, Beaker can trust that dat://taravancil.com should point to dat://6dff5cff6d3fba2bbf08b2b50a9c49e95206cf0e34b1a48619a0b9531d8eb256.
To make your new site available to readers, all you really have to do is send your site's Dat link to someone else.
Fun fact: You can share any files in your library, including the Beaker AppImage!
Sharing your link on social media will begin to generate traffic as well.
You are now part of the P2P Web!
Be aware that your website is only online when the Dat files are online. Unless someone else is seeding your site, it shuts down when your computer does. So, encourage your peers to seed forever. One way around this limitation is Hashbase.io, "Hosting for the peer-to-peer Web".
Beaker is still a project in infancy. Dat is a little further ahead, but both projects could use some help. Here are some ways you can pitch in:
Mike McCallister has written about Linux and FLOSS since the turn of the millennium. Find him at michaelmccallister.com, Author.MichaelMcCallister on Facebook, and @workingwriter at Twitter and most everywhere else online.